In women, periods or menstrual cycle is a vital phase that occurs in the female reproductive system. It provides important hormones to keep the female body healthy. The menstrual period is essential for the formation of oocytes and the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. The menstrual flow usually occurs after 25-30 days and lasts two to seven days. Irregular periods, abnormal or no bleeding imply abnormal ovulation or a state of anovulation.
What is anovulation?
Anovulation is a condition when the ovaries fail to release an egg or oocyte during a menstrual cycle due to which ovulation does not take place. Women facing anovulation problem have more or less irregular periods. Severe anovulation condition is one of the most common causes of infertility.
Besides, chronic anovulation can exacerbate long-term problems such as hyperandrogenism or osteopenia. It is a low-bone density state which causes weakening of bones. Besides, anovulation is responsible for multiple imbalances and improper functionality of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Abnormal ovulation can lead to fertility problems. However, the irregular period problem can be treated with fertility drugs unless you are not diagnosed with other health conditions such as thyroid or abnormalities of adrenal or pituitary glands.
What is the cause of irregular periods?
On average, the ovulation period of a woman occurs every 24 to 38 days and may last until seven days. Some women face irregular period problem in the following scenarios:
- The in-between period may start changing.
- The bleeding that occurs during periods may be more or less than usual.
- The period of each menstrual cycle may vary a lot.
Various factors can disrupt the normal pattern of your periods. These include:
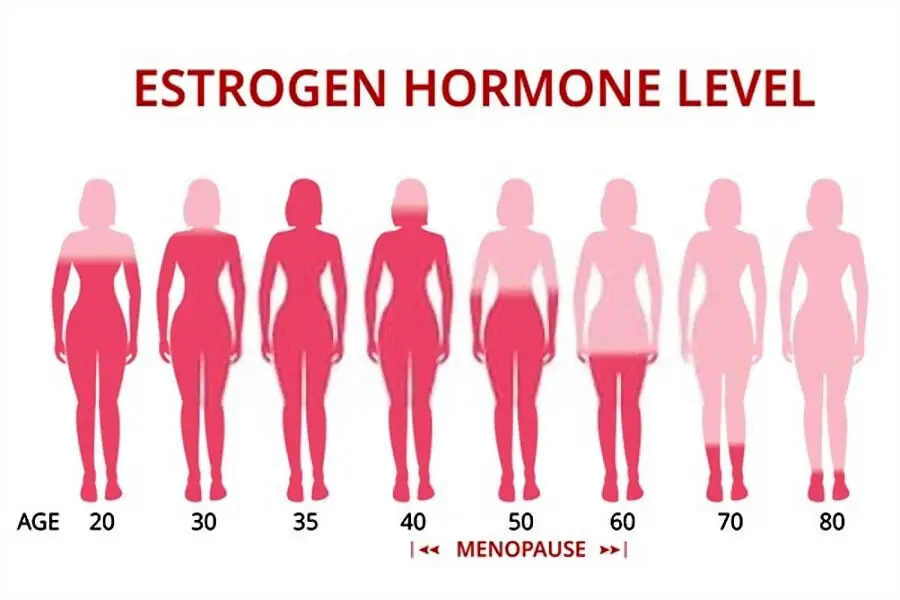
- Change in the body’s level of estrogen and progesterone hormones. This is usually observed as a common cause of irregular periods for young girls going through puberty and women approaching menopause.
- He presence of an intrauterine device (IUD) or a contraceptive device fitted inside the uterus. It is a T-shaped coil-like birth control device inserted in a woman’s body to control pregnancy.
- In case you have a rigorous exercise routine, you may experience irregular periods.
- Changing the brand or dosage of birth control pills or using other medications.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that causes enlargement of ovaries along with small cysts on the outer edges. PCOS may occur as a combination of genetic problems and environmental factors.
- Pregnancy or Breastfeeding babies may sometimes lead to irregular periods. This is so because prolactin, a hormone responsible for breast milk production suppresses reproductive hormones resulting in light or no periods.
- Perimenopause is a transition phase before menopause. Fluctuating estrogen levels during this period can cause irregularity in the menstrual cycle.
- Stress can cause temporary interference with the part of the brain that controls period causing hormones.
- Uterine fibroids or muscular tumors may develop in the wall of uterus causing painful and heavy periods.
- Uterine lining thickening
- Overactive thyroid or hyperthyroidism can cause shorter and light periods.
- Underactive thyroid or hypothyroidism can cause fatigue and weight gain and also long and heavy periods and increased cramping.
- Obesity and excess weight gain
- Severe scarring or adhesions of the lining of the uterus
- Certain medications can lead to irregularity in periods that include blood thinners, antidepressants, epilepsy drugs, chemotherapy drugs, aspirin, and ibuprofen.
Do periods indicate fertility?
Having regular periods simply indicates a high chance of fertility. In general, a woman can get pregnant during ovulation which occurs around 10-15 days before the next menstrual cycle. Ovulation is the process of egg release from the ovaries.
During periods, one or more eggs develop and get released during the cycle. After ovulation, the egg lives for 24 hours. Pregnancy occurs if male sperms meet with the fertilized egg of the female. With increasing age, the menstrual cycle becomes irregular or short and the lining of the womb may become thin. Also, the ability to nurture a fertilized egg may be affected.
Irregular Periods and Pregnancy Signs
The menstrual cycle usually occurs during puberty which occurs between 10-15 years of age and continues till menopause which is between 45-55 years of age. Irregularity in periods, also known as oligomenorrhea, may occur if there is hormonal imbalance, changes in contraception method, etc. It can also lead to a problem with fertility.
However, this is not always true. To track ovulation and the length of the cycle, one can do either of the following:
- Mark your period dates on the calendar and observe the patterns.
- Observe the changes in cervical mucus. As the ovulation phase occurs, the mucus will become more slippery, clear and catchy.
Getting pregnant with an abnormal period pattern is difficult. Some of the signs for prediction of ovulation include:
- An increase in cervical mucus: You may observe clear and stretchy fluid discharging from the vagina or when you wipe after using the washroom. This indicates that ovulation is near.
- An increased body temperature: Track and observe your body temperature before you eat, talk or wake up for a month. It may help to understand your body’s typical timing for ovulation in future cycles.
How to get pregnant with irregular periods?
With irregular periods, the chances of pregnancy become low. However, certain measures can help which include:
- Having intercourse at least every two to three days.
- Consult your doctor for treatment of the condition to increase the chances of pregnancy. Drugs such as Clomid or clomiphene citrate are prescribed to induce ovulation.
- Adopting a healthy routine with regular exercise can help gain or lose weight. Consult your doctor for recommendation s and meal plans and guidelines for exercise.
- In case the occurrence of irregular periods is due to an underactive or overactive thyroid problem, your doctor will prescribe you medications such as levothyroxine (Levoxyl, Synthroid, Unithroid) to increase or decrease the thyroid hormone in the body.
Author: Dr. Deepti Asthana has been associated with Fortis Memorial research institute Gurgaon for the past four years and is working as a consultant there at present.

Leave a Reply